space observatory
From Spacefaring
A space telescope is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid several problems caused by the atmosphere, including the absorption or scattering of certain wavelengths of light, obstruction by clouds, and distortions due to atmospheric refraction such as twinkling. Space telescopes can also observe dim objects during the daytime, and they avoid light pollution which ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky, and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct from Earth imaging satellites, which point toward Earth for satellite imaging, applied for weather analysis, espionage, and other types of information gathering.
Wikimedia, Wikidata
space observatory
Advanced Composition Explorer, astrometry satellite, Dong Fang Hong 2, Ekran, liquid mirror space telescope, Orbiting Solar Observatory, X-ray astronomy satellite, X-Ray Timing and Polarimetry Mission,
-
Location: KML, Cluster Map, Maps,
-
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory ⓘ
space observatory -

STARS-AO ⓘ
Japanese CubeSat space telescope -

ASTERIA ⓘ
CubeSat testing technologies for the detection of exoplanets -

astrometry satellite ⓘ
artificial earth satellite that performs astrometry tasks -

Far Ultraviolet Space Telescope ⓘ
FAUST is a compact, wide field-of-view, far ultraviolet instrument designed for observations of extended and point sources of astronomical interest. It was originally used in sounding rocket work by both French and American investigators. -

High Energy Transient Explorer ⓘ
space observatory -

liquid mirror space telescope ⓘ
space telescope which uses a reflecting liquid such as mercury as its primary reflector -

Orbiting Astronomical Observatory ⓘ
series of four space observatories launched between 1966 and 1972 -

STEREO-A ⓘ
NASA heliophysics space probe -

STEREO-B ⓘ
former NASA heliophysics space probe -

X-ray astronomy satellite ⓘ
satellite involved in X-ray astronomy -

X-Ray Timing and Polarimetry Mission ⓘ
science mission designed to study the state of matter under extreme conditions of density, gravity and magnetism -

Orbiting Solar Observatory ⓘ
series of American solar space observatories
| Type | Subtype | Date | Description | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| class | orbit | Solar and Heliospheric Observatory | solar probe, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | orbit | STARS-AO | CubeSat, nanosatellite, space telescope, technology demonstration spacecraft, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | ASTERIA | CubeSat, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | astrometry satellite | space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | Far Ultraviolet Space Telescope | space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | High Energy Transient Explorer | space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | liquid mirror space telescope | liquid mirror telescope, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | Orbiting Astronomical Observatory | space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | STEREO-A | solar probe, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | STEREO-B | former entity, solar probe, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | X-ray astronomy satellite | research satellite, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | space instrument | X-Ray Timing and Polarimetry Mission | X-ray telescope, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| class | spaceflight | Orbiting Solar Observatory | solar observatory, space telescope, | Wikidata | |
| commons | image | ASCA | Commons | ||
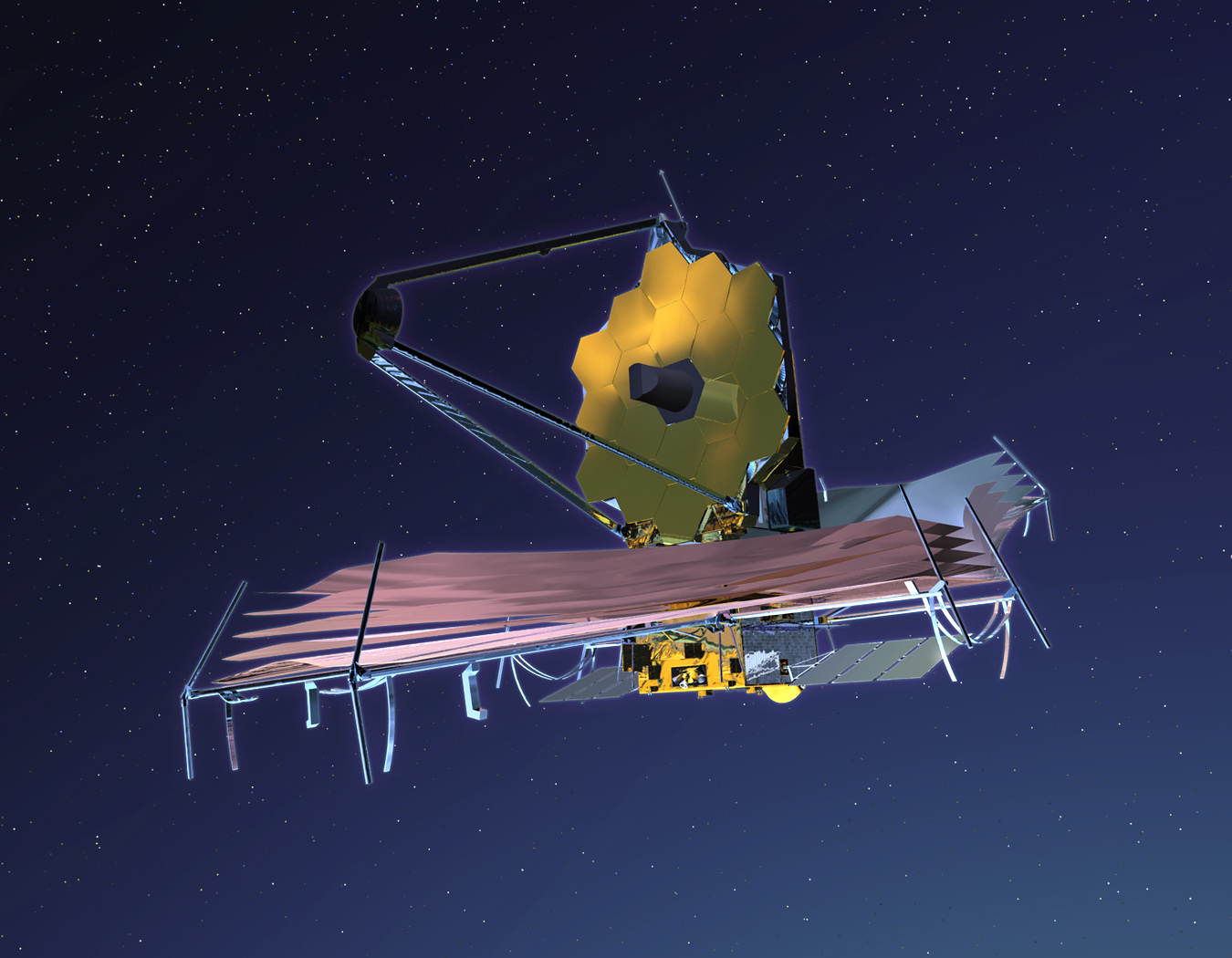
| commons | image | James Webb, Space Telescope | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Wavelength Sensitivity of Hubble, Webb, Roman, and Other Observatories (01FEBQTM8Y4FESTQ4N2AFQDBXH) | Commons | ||
| commons | image | G111 021 000946 | Commons | ||
| commons | image | OldestStar-SM0313-SMSSJ031300366708393-20140210 | Commons | ||
| commons | image | SAFIR-CALISTO | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Skylab Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) No.1 Telescope graphic (0101909) | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Skylab Hydrogen-Alpha (H-Alpha) No.2 Telescope graphic (0101910) | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Skylab 2 Weitz UV Stellar Astronomy Experiment | Commons | ||
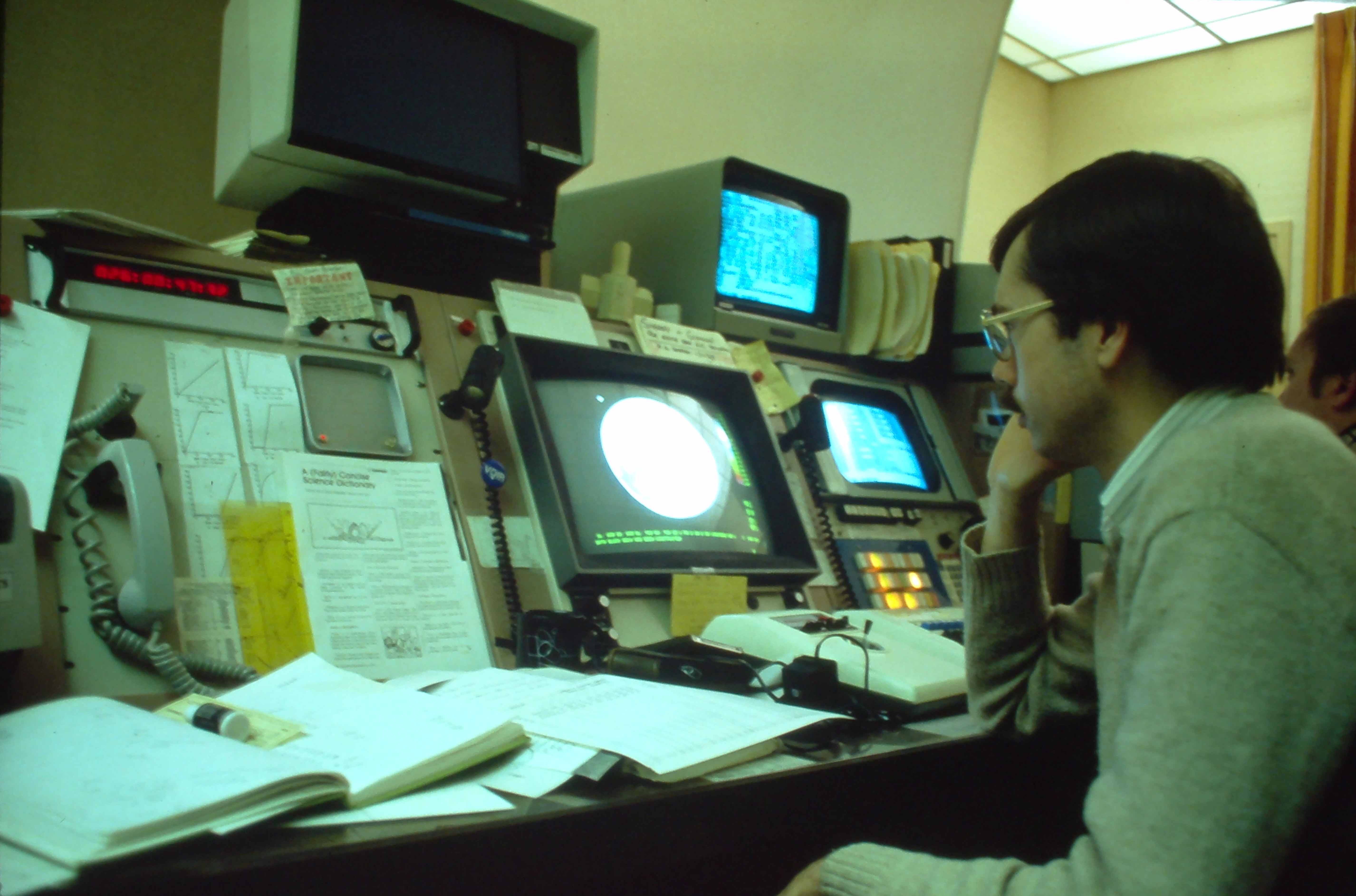
| commons | image | Ground stations at Goddard and VILSPA controlled IUE. Goddard’s console is shown with observer Gary Ferland. The model IUE was used to visualize its orientation and the joystick made small corrections to the pointing. | Commons | ||









