Giotto
From Spacefaring
Q660356
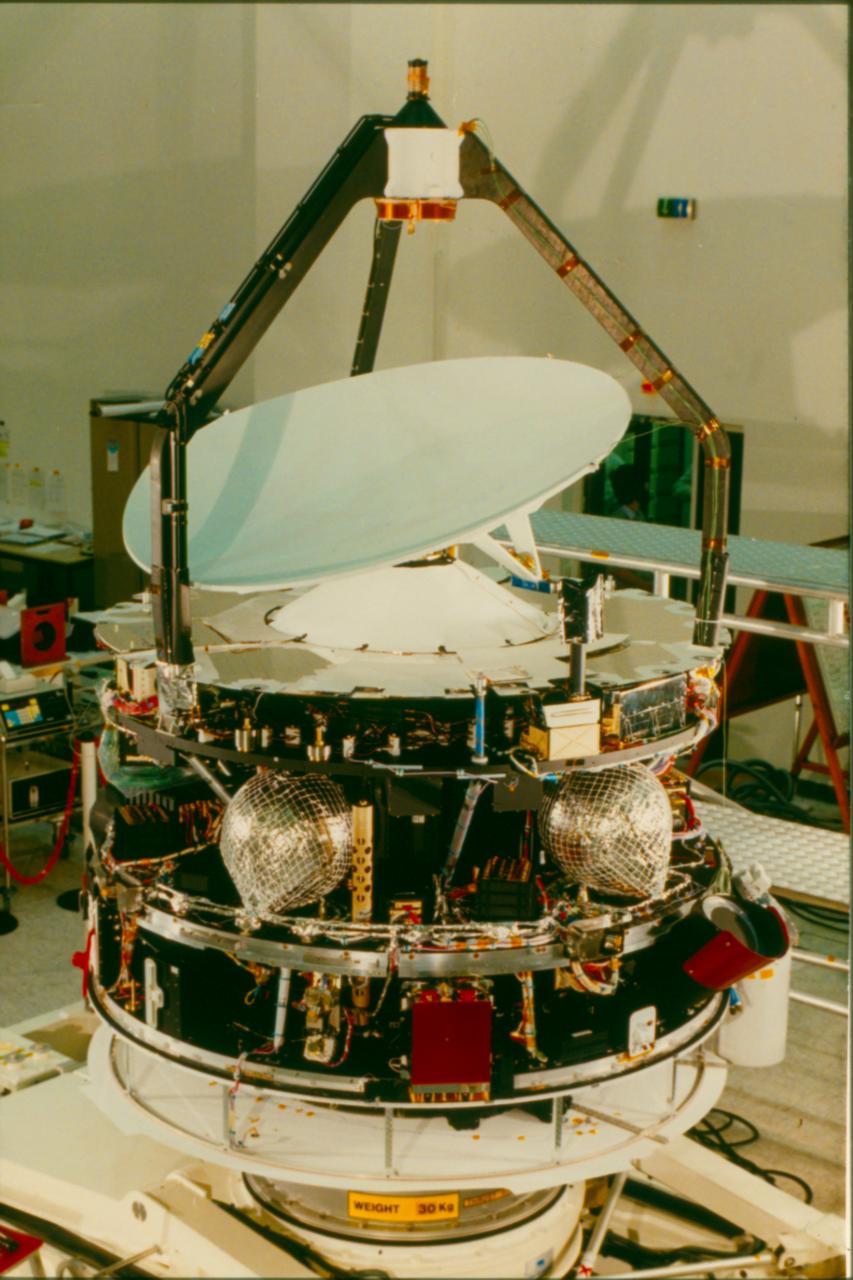
Giotto was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency. The spacecraft flew by and studied Halley's Comet and in doing so became the first spacecraft to make close up observations of a comet. On 13 March 1986, the spacecraft succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers. It was named after the Early Italian Renaissance painter Giotto di Bondone. He had observed Halley's Comet in 1301 and was inspired to depict it as the star of Bethlehem in his painting Adoration of the Magi in the Scrovegni Chapel.
1985-07-02T00:00:00Z
1985-07-02T00:00:00Z
1985 Giotto
1990-07-02T00:00:00Z
1990-07-02T00:00:00Z
gravity assist
1985-07-02T00:00:00Z
1985-07-02T00:00:00Z
rocket launch
1986-03-14T00:00:00Z
1986-03-14T00:00:00Z
flyby
1992-07-23T00:00:00Z
1992-07-23T00:00:00Z
service retirement
1992-07-10T00:00:00Z
1992-07-10T00:00:00Z
flyby
{"selectable":false,"showCurrentTime":false,"width":"100%","zoomMin":100000000000}
- First results from the Giotto magnetometer experiment at comet Halley - scientific article published in Nature, Q1860, 1986
- Giotto observations of the bow shock at Comet Halley - , Q1860, 1986
- Dust density and mass distribution near comet Halley from Giotto observations - scientific article (publication date: 15 May 1986), Q1860
- The Giotto encounter with comet Halley - scientific article published in Nature, Q1860, 1986
| Type | Subtype | Date | Description | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| commons | image | FRG 1986 MiNr1273 SD B002 | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Comet Halley at Giotto spacecraft's closest approach | Commons | ||
| commons | image | In 1986, the European spacecraft Giotto became one of the first spacecraft ever to encounter and photograph the nucleus of a comet, passing and imaging Halley's nucleus as it receded from the sun. | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Giotto Whipple shield ESA239195 | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Comet Halley close up-cropped | Commons | ||
| commons | image | 1986 Comet Halley | Commons | ||