F-1
From Spacefaring
Q73658
The F-1 is a rocket engine developed by Rocketdyne. The engine uses a gas-generator cycle developed in the United States in the late 1950s and was used in the Saturn V rocket in the 1960s and early 1970s. Five F-1 engines were used in the S-IC first stage of each Saturn V, which served as the main launch vehicle of the Apollo program. The F-1 remains the most powerful single combustion chamber liquid-propellant rocket engine ever developed.
Wikimedia, Wikidata
Rocketdyne F-1; Rocketdyne F1
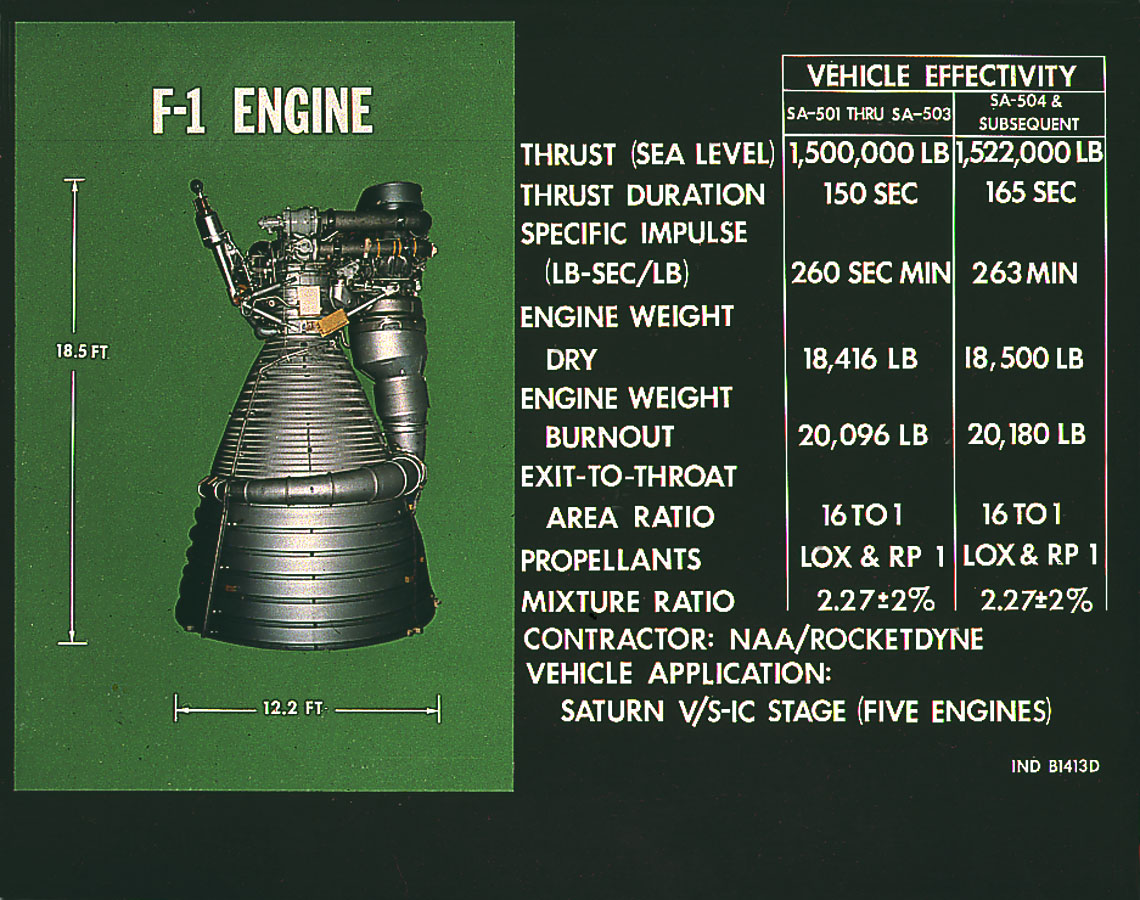
diameter 3.76 metre, height 5.79 metre, mass 8391 kilogram, mass 8353 kilogram, maximum thrust 1522000 pound-force, maximum thrust 1500000 pound-force, specific impulse by weight 260 second, specific impulse by weight 263 second,
Rocketdyne, United States,
United States, Dong Fang Hong 2, Ekran, rocket engine, [[F-1|]],
-
Location: KML, Cluster Map, Maps,
| Type | Subtype | Date | Description | Notes | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| commons | image | SaturnV S-IC | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Rocketdyne F-1 used baffle | Commons | ||
| commons | image | F-1 big | Commons | ||
| commons | image | SaturnV S-IC (cropped) | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Werner Von Braun standing next to the five F-1 engines of a Saturn V first stage | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Werner Von Braun standing next to the five F-1 engines of a Saturn V first stage | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Test Firing of a Rocketdyne F-1 Engine, Edwards Air Force Base | Commons | ||
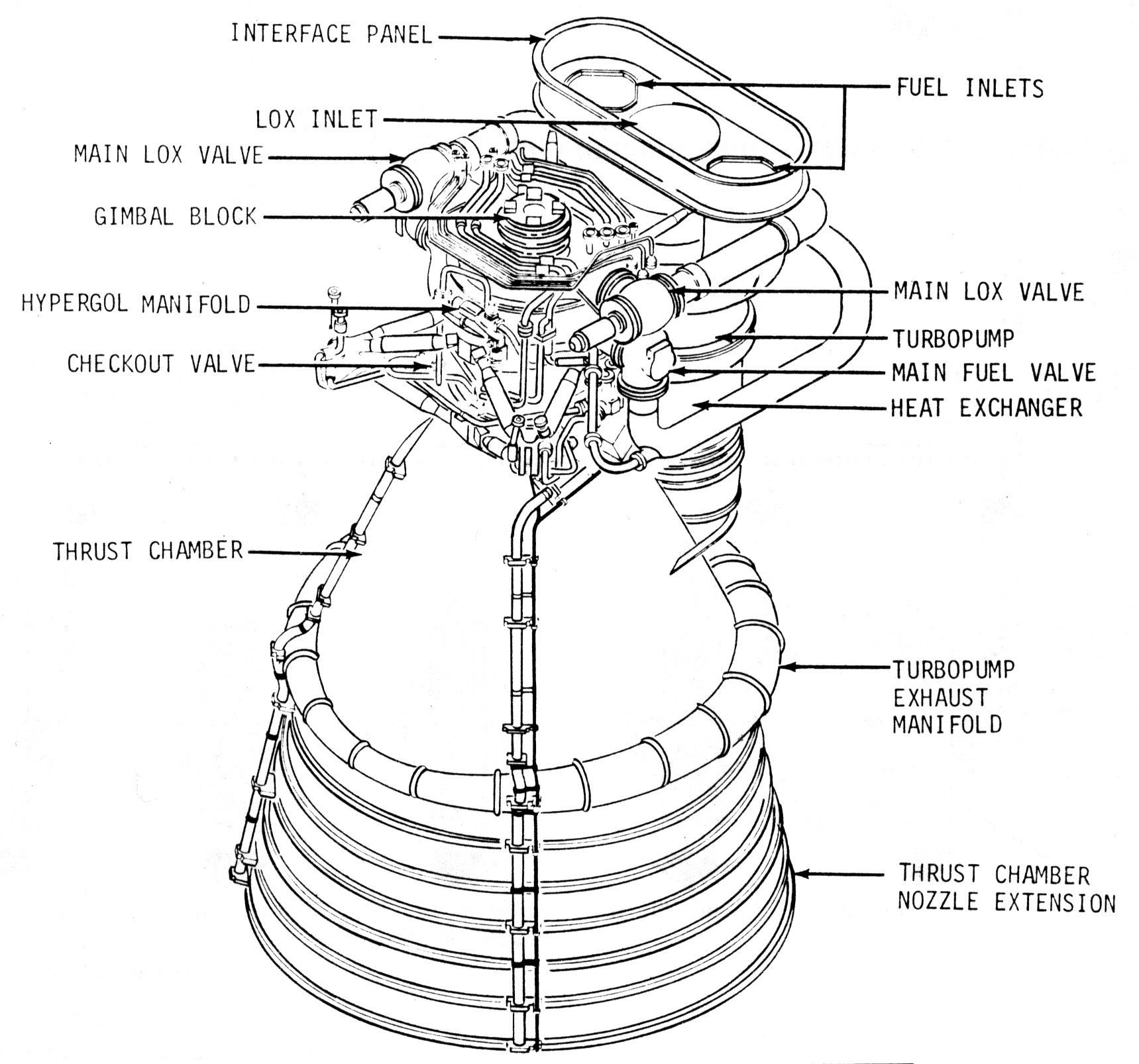
| commons | image | Rocketdyne F-1 rocket engine diagram | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Test Firing of a Rocketdyne F-1 Engine, Edwards Air Force Base | Commons | ||
| commons | image | Rocketdyne F-1 rocket engine diagram | Commons | ||